Tevety
The Phases of the Earth's Moon
The Phases of the Earth's Moon
Couldn't load pickup availability
 Free Fast Shipping over Rs.799
Free Fast Shipping over Rs.799
 Exchangeable for same item only.
Exchangeable for same item only.
 Customer Support
Customer Support
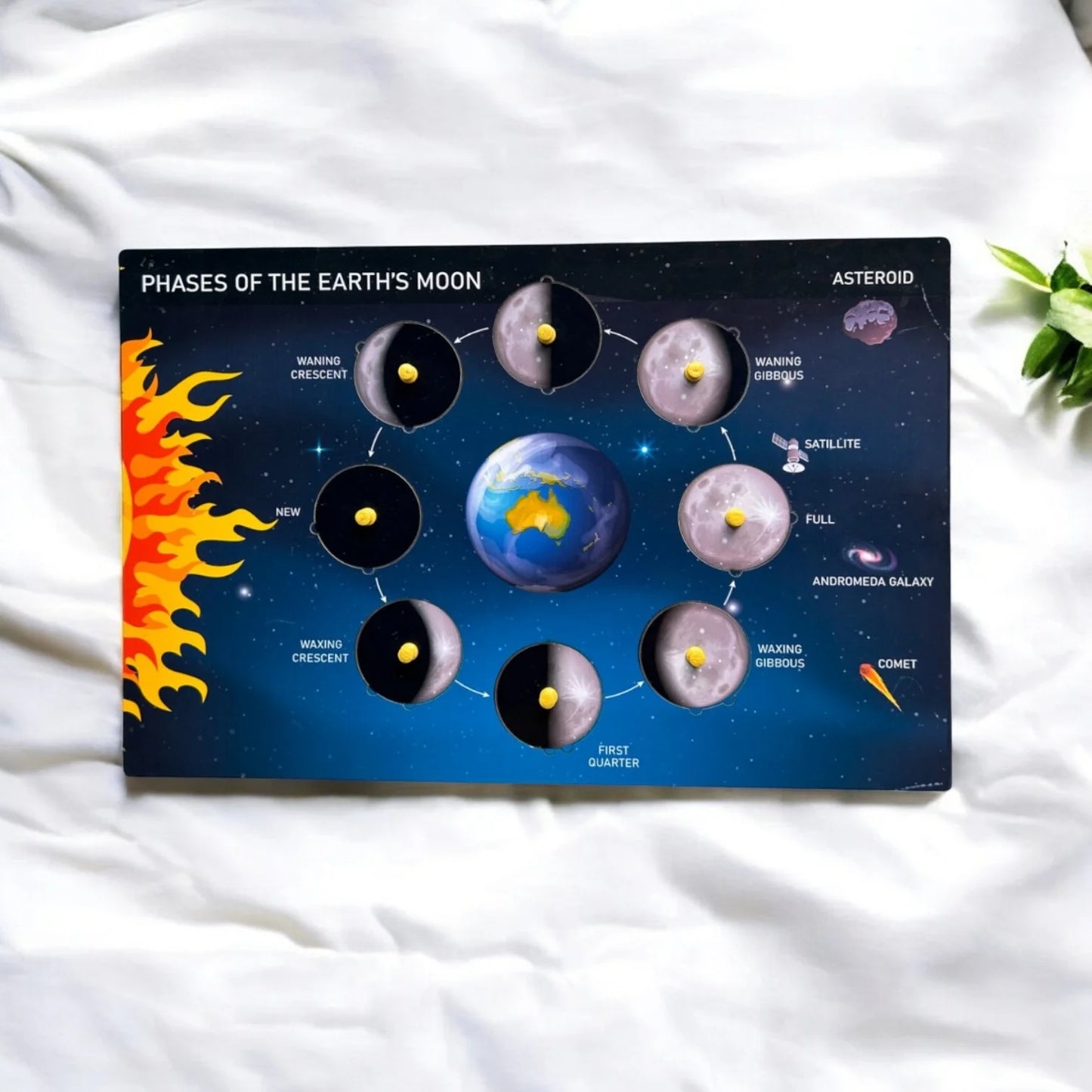
Phases of the Earth’s Moon Board:
Over view: The phases of the Moon, a 29.5-day cycle, start with the New Moon and progress through Waxing Crescent, First Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, Last Quarter, and Waning Crescent, before returning to the New Moon. These phases are caused by the Moon’s orbit around Earth and its changing position relative to the Earth and Sun.
New Moon: The Moon is between Earth and the Sun, and the side of the Moon facing Earth is not illuminated, making it invisible in the night sky.
Waxing Crescent: A small sliver of the Moon starts to become visible. This phase occurs when the Moon is a bit to the east of the Sun and a thin crescent is visible on the right side.
First Quarter: Half of the Moon is illuminated and visible from Earth. This phase occurs when the Moon is at a 90-degree angle with respect to the Earth and Sun, so we see exactly half of the Moon’s lit surface.
Waxing Gibbous: More than half of the Moon is illuminated but it’s not yet full. It’s growing (‘waxing’) towards a full moon, with the illuminated portion increasing each night.
Full Moon: The entire face of the Moon that faces Earth is illuminated by the Sun, making the Moon appear as a full circular disc in the night sky.
Waning Gibbous: After the full moon, the light starts to decrease (‘wane’), but more than half of the Moon’s face is still illuminated.
Last Quarter: Similar to the first quarter, but the opposite half of the Moon is illuminated. It’s the reverse of the first quarter.
Waning Crescent: The Moon is returning to the new moon phase, and only a small crescent on the left side is illuminated.
Skill Development: Astronomy Knowledge Observation Skills Critical Thinking Spatial Awareness Memory Retention Hands-On Learning
To effectively use the Moon phases model, students should regularly align the model with the current lunar phase, observe the actual Moon for comparison, keep a journal of their observations, engage in group discussions for collaborative learning, research the science behind Moon phases, and integrate this learning with broader science topics. This approach enhances understanding of the lunar cycle and its scientific context.
This item is only exchangeable for the same , if available, and cannot be returned
Share